- OP Labs formerly Oxford Peptides.
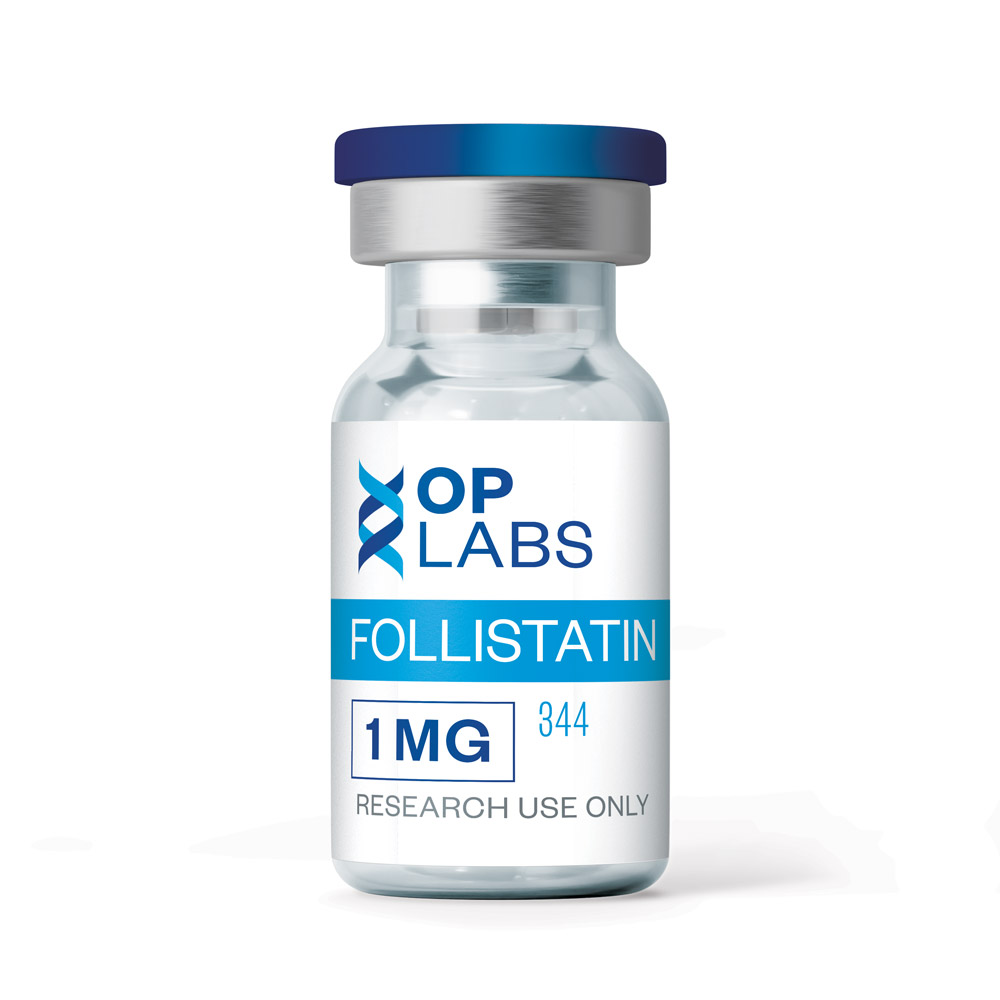
- Batch HPLC tested at 99%+ purity.
- Store frozen long term or in fridge when ready to be used.
- Sold for research purposes only.
- Contact us for Wholesale Orders.
Download COA here: Follistatin344_1mg.pdf
Please note if you have a different Batch ID please contact us for the latest COA.
Follistatin-344
- Protein Name: Follistatin-344 (FS-344)
- UniProt ID: P19883 (Human Follistatin isoform 1)
- Gene: FST
- Amino Acid Length: 344 residues
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 38 kDa (varies with glycosylation)
- Structure:
- Follistatin-344 is a glycoprotein with multiple follistatin domains, including three follistatin-like domains (FSD1, FSD2, FSD3) and a C-terminal domain.
- Composed primarily of alpha-helices and beta-sheets forming a compact globular structure.
- Contains multiple disulfide bridges contributing to its tertiary structure stability.
- Has multiple N-linked glycosylation sites impacting molecular mass and function.
- Functionally Important Regions: The three follistatin-like domains mediate binding interactions with TGF-β superfamily ligands.
- Synthesis: Recombinant expression typically performed in mammalian or insect cells to preserve post-translational modifications.
- Physicochemical Properties: Predicted isoelectric point (pI) ~ 4.5–5.0; stable tertiary structure due to disulfide bonding.
References
- Shimasaki S, et al. “The role of follistatin in the regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion and folliculogenesis.” *Endocrine Reviews*, 1997;18(6): 803-823. DOI: 10.1210/edrv.18.6.0314.
- Cash JN, et al. “Structural basis for antagonism of human activin by follistatin: crystal structure of the follistatin–activin complex.” *Genes & Development*, 2009;23(21): 2809–2817. DOI: 10.1101/gad.1845709.
- UniProt Consortium. “UniProtKB – P19883 (FST_HUMAN).” https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P19883
- Goebel EJ, et al. “Follistatin: a glycoprotein with multiple biological activities.” *Cellular Signalling*, 1993;5(6): 599-606. DOI: 10.1016/0898-6568(93)90027-X.
Keywords: Follistatin-344








Anonymous –
chen yu tsang –
Good package sizs
Michal L. –
The product is good… unfortunately, when I wanted to buy the next one… the price was higher by £20
I also bought other products but also when I wanted to buy them again the price increased!!!
Mihai T. –
Amazing results!! Joint and articulations got stronger and appetite improved 10/10
Sammy Ashry –
Love this. But use sparingly to be safe. 10-20 days on and 6-8 weeks off.
Dan Dediu –
I have order folistatin but i have received something else.
clickanddrop –
If there is an issue with the order just let us know. Some packing mistakes are inevitable.
Hugh –
Ordered 2 eventually recieved 1 and others I did not order.
clickanddrop –
If there is an issue with the order just let us know. Some packing mistakes are inevitable.
Steven Saxton –
Dale S. –
Good quality follistatin
Anonymous –
Waiting to try this, but the peptides are of high quality from this website